

Where the transformation was performed prior to fitting. On the contrary, it fails if we coded the model as: logCount ~ Insecticide It means: it is ok if we coded the model as: log(Count) ~ Insecticide It is enough to set the argument ‘transform’ to ’response, although the transformation must be embedded in the model. With R, we can use the ‘emmeans’ package (Lenth, 2016): library(emmeans)ĬountM <- emmeans(model, ~Insecticide, transform = "response")
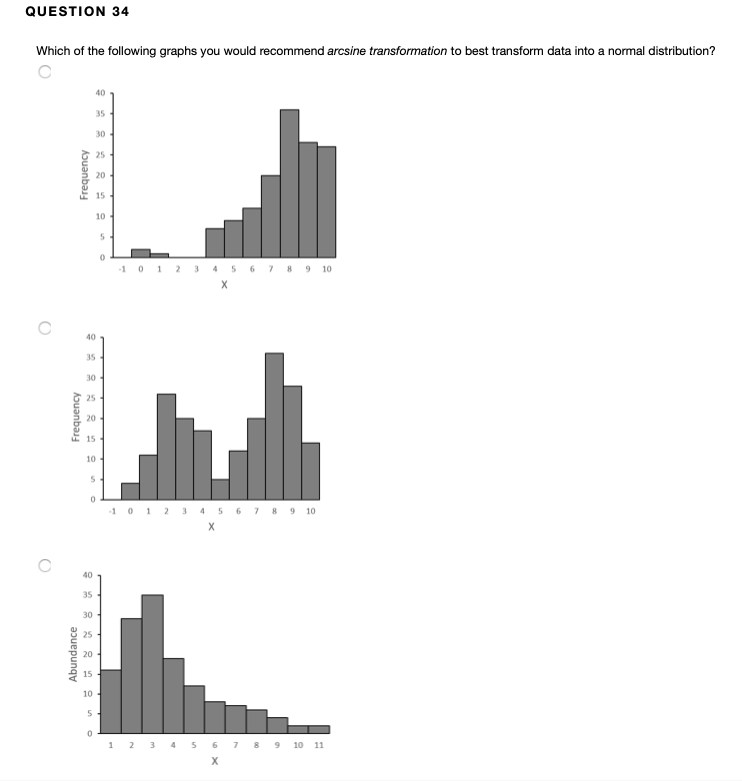
#Arcsine transformation in r software
This ‘manual’ solution is always available, regardless of the statistical software at hand. This may be simply done by hand, with e.g \(exp(6.343) \times 0.178 = 101.19\) (for insecticide A). multiply it by the standard error of the transformed data.take the first derivative of the back-transform function and.No worries, we can use the delta method to back-transform standard errors. However, this leaves us with the problem of adding a measure of uncertainty to back-transformed means. We suggest that the use of the second method. Back-transformed means ‘estimate’ the medians of the original populations, which may be regarded as better measures of central tendency for skewed data. Accordingly, if we have done, e.g., a logarithmic transformation, we can exponentiate the means of transformed data and report them back to the original measurement unit. Furthermore, please remember that the means of original data may not be a good measure of central tendency, if the original population is strongly ‘asymmetric’ (skewed)! This is clearly less than optimal, if we want to suggest more than the bare variability of the observed sample.
We can present the means of the original data with standard deviations.What should we do, then? Here are some suggestions.
Unfortunately, we loose clarity: how many insects did we have on each leaf? If we present in our manuscript a table like this one we might be asked by our readers or by the reviewer to report the means on the original measurement unit. In the end, we might show the following table of means for transformed data: Insecticide In this example, the standard error for each mean (SEM) corresponds to \(\sqrt\). # Residual standard error: 0.3973 on 12 degrees of freedom # lm(formula = log(Count) ~ Insecticide, data = dataset) Consider the following dataset, that represents the counts of insects on 15 independent leaves, treated with the insecticides A, B and C (5 replicates): dataset F)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
